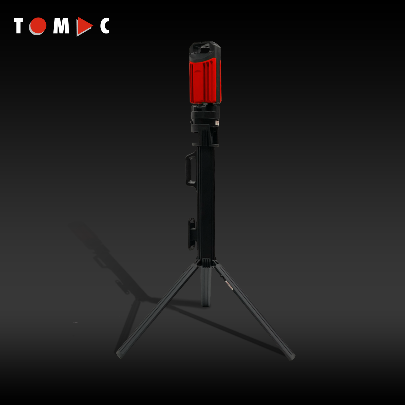
LED High Bay Lights: The Core Solution for Industrial Work Light Applications
What Are LED High Bay Lights and How Do They Support Industrial Lighting Design?
High bay LED lights hang from ceilings in places where the space between floor and roof goes over 20 feet tall. Think warehouses, factories, and those big distribution hubs we all rely on. These lights throw out really strong, targeted beams that spread evenly throughout massive open spaces. Switching from old school metal halide systems to LED technology cuts down power usage somewhere around half to three quarters, plus they maintain brightness better over time and turn on instantly when needed. The way these lights are designed focuses the illumination so there are fewer shadows and less annoying glare bouncing around. This makes a huge difference for workers doing detailed work like putting things together, checking quality, or operating machinery safely.
Key Differences Between High Bay and Low Bay Lighting in Manufacturing Facilities
What really sets these lighting options apart comes down to where they go and how they spread their light. High bay lights work best when installed in areas that are at least 20 feet high. These fixtures have narrow beams, usually around 60 degrees or smaller, which helps focus the light straight down from those great heights. On the flip side, low bay lights hang out below that 20 foot mark and need wider beams to get good coverage across shorter vertical distances. Take a look at industrial settings for instance. A high bay light putting out about 30,000 lumens will do wonders for lighting up those robotic welding spots in big open factories. Meanwhile, the low bay versions tend to be much better suited for places like packaging lines where ceilings aren't so high but workers need light spread out over larger horizontal areas.
Brightness and Lumens in Industrial Lighting: Matching Output to Workspace Needs
The amount of light needed depends heavily on what kind of work is being done. For instance, when workers need to inspect products closely during quality checks, they typically require around 100 to 150 lux (about 9 to 14 foot candles) for good visibility. Storage rooms where items are just kept don't need nearly as much light, functioning well with about 50 lux (roughly 5 foot candles). Modern LED high bays address this range of needs thanks to their dimming capabilities and variable output settings. Facilities can adjust brightness according to what's happening in different areas throughout the day. The flexibility not only makes it easier for employees to see what they're doing but also cuts down on electricity costs without compromising safety standards in manufacturing spaces that change constantly throughout operations.
Case Study: LED Factory Lighting Upgrade in an Automotive Assembly Plant
A car manufacturing facility located near Chicago swapped out around 800 old metal halide lights for LED high bay units last year. They saw their energy bills drop by roughly 62 percent, which translates to about $280k saved each year on electricity costs alone. Fewer people had to call maintenance too since these new lights lasted longer without burning out. Factory workers mentioned they weren't squinting as much anymore after long hours on the line, something that apparently helped boost productivity during quality checks by approximately 12%. Plus, the whole shop now has much better light distribution throughout all areas, making it easier to spot defects and operate machinery safely without shadows getting in the way.
Trend Analysis: Shift Toward Smart LED High Bay Systems with Motion Sensors
More and more factories are jumping on the smart lighting bandwagon these days. About half again as many new setups (we're talking around 55%) now feature those fancy IoT LED high bays that come packed with occupancy sensors and daylight harvesting tech. What happens? Well, these clever systems just tweak the brightness depending on what's going on right then and how much natural light there is outside. In places where people don't hang out much, like those long storage aisles, energy consumption drops dramatically sometimes as much as 80%. And when companies hook these lights into their broader energy management systems across the whole building, the money saved gets even better. For plant managers watching their bottom line while trying to meet green targets, this kind of upgrade makes both financial and environmental sense.
Illuminance, Uniformity, and Compliance with Industrial Lighting Standards
ANSI and IES Lighting Standards for Industrial Workspaces: A Compliance Guide
For industrial lighting setups, following the ANSI/IES RP-7-21 guidelines is pretty much essential since they set out what counts as adequate light levels both for worker safety and getting things done efficiently around the plant. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration says at least 5 foot candles should be present across regular workspaces. Meanwhile, when it comes to places where folks need to do close up work like putting together small parts or inspecting products, the Illuminating Engineering Society suggests somewhere between 75 to even 100 foot candles might be needed. Sticking with these rules helps companies dodge fines that can run into thousands of dollars each time there's a problem. Plus, better lighting actually makes sense beyond just avoiding trouble. Studies from the IES Lighting Handbook published last year show workplaces see error rates drop anywhere from 18% down to about 22% when proper illumination standards are met.
Recommended Illuminance Levels by Task Type and Work Zone
| Work Area | Minimum Illuminance | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Warehousing (aisles) | 20 fc | 20-30 fc |
| Machinery Assembly | 50 fc | 75-100 fc |
| Quality Inspection Stations | 100 fc | 100-150 fc |
| Material Storage | 5 fc | 5-10 fc |
High-risk environments such as robotic work cells often require 200+ fc to ensure precise visual monitoring and operator safety, surpassing baseline regulatory thresholds.
Uniformity Ratio and Lighting Distribution: Ensuring Consistent Coverage Across Floors
The ideal lighting setup should maintain a maximum 4 to 1 uniformity ratio, which basically means the brightest spot shouldn't be more than four times brighter than the dimmest area. This helps avoid those glaring contrasts that make people squint and cause eye strain over time. LED high bays actually hit around 3:1 ratios thanks to their specially designed lenses and reflectors. Metal halide systems? They usually struggle with much worse ratios, often sitting around 6:1 on average. When warehouses stick to these IES standards for light distribution, they tend to see some pretty impressive results. Studies show about 31 percent drop in slips and falls, plus workers complete tasks 14% quicker in areas where materials get handled because everything just looks clearer and spaces feel more navigable.
Color Temperature and CRI: Optimizing Visual Clarity and Worker Performance
How Color Temperature Affects Alertness and Precision in Production Zones
Cool white light in the 4000 to 5000K range acts almost like real daylight and actually helps people stay more alert and think better when working in factories or workshops. Research from NIH back in 2019 showed something interesting too. Workers who were in areas lit with 5000K light reacted about 18 percent quicker on detailed jobs than folks sitting under warmer 3000K lighting. Looking at recent guidelines, the IES updated their recommendations in 2023 suggesting companies should match lighting colors to specific tasks. They advise using those higher Kelvin numbers in places where things need to be assembled or inspected carefully because it really does help concentration and cuts down mistakes made by humans.
Importance of Color Rendering Index (CRI) in Quality Inspection Tasks
Getting accurate colors matters a lot when small variations can mean something's wrong or dangerous. LED work lights that have at least an 80 CRI rating show colors about 30 percent better than regular lights, making it much easier to spot problems in things like material quality, paint jobs, or label printing. We saw this firsthand in the auto industry back in 2022. When they switched to lighting with CRI ratings over 90, their mistake rate during inspections dropped by around 35%. For folks working with electronic parts, this kind of lighting makes all the difference. Many components rely on color codes to function properly, so being able to see those distinctions clearly isn't just helpful—it's practically essential for avoiding costly mistakes down the line.
Balancing Visual Comfort and Performance During Extended Shifts
Cooler light colors definitely help people focus better, but staring at them for too long can really give workers a headache. The folks at OSHA put out some guidelines back in 2021 suggesting workplaces mix general lighting around 3000 to 4000K with brighter 5000K lights right where tasks happen. This combo keeps employees alert without making their eyes sore. Modern LED setups that can change color throughout the day have made a big difference. Factories reporting up to a 27% drop in tired eyes during those long 12 hour shifts. For anyone designing lighting in industrial spaces, getting the ANSI/IES RP-7-22 standards right means paying attention to how well colors render, what temperature feels comfortable, and making sure the light spreads evenly everywhere. Getting these basics right isn't just about following rules it actually makes a real difference in how workers feel day after day.
Durability and Reliability of LED Work Lights in Harsh Industrial Conditions
IP Ratings and Thermal Management Under Extreme Environmental Stress
For industrial LED lighting to work properly in tough manufacturing settings, they need at least an IP65 rating so they can handle dust, moisture, and chemicals without failing. Better quality units typically come with aluminum housing and special cooling systems that actually move heat away around 30 percent faster compared to standard models. What does this mean? The lights stay brighter longer since their output doesn't drop off as much over time. Even when temperatures climb past 122 degrees Fahrenheit (which is about 50 Celsius), these fixtures maintain roughly 95% of their original brightness according to recent testing done last year on material performance across different conditions.
Vibration Resistance and Impact Protection Near Heavy Machinery
LED work lights really stand out in places where there's constant vibration, such as inside steel mills or along busy assembly lines. The solid state design means no delicate filaments or moving components to break, and those special shock absorbing mounts cut down on failures by almost 90% when compared with old HID lighting systems. These lights come equipped with tough polycarbonate lenses and heavy duty housings that can take a beating from regular mechanical impacts and vibrations reaching around 10G forces. That kind of toughness makes them dependable even under the harshest conditions found in most industrial environments today.
Long-Term Reliability: Failure Rates of LED vs. Traditional Lighting in Steel Mills
- LED failure rate: 0.7% over 15,000 hours (Ponemon Institute 2023)
- Metal halide failure rate: 18.2% over same period
A 2022 retrofit at a steel mill demonstrated that switching to LED work lights cut annual maintenance costs by $74,000 and reduced downtime despite operating 14+ hours daily. With lifespans reaching 100,000 hours—over six times longer than high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps—LEDs minimize disruptions caused by frequent relamping and ballast replacements.
Energy Efficiency, Maintenance Reduction, and ROI of Industrial LED Work Lights
Lifecycle Cost Comparison: LED vs. Metal Halide in Large-Scale Facilities
Switching from metal halide lighting to LED work lights cuts down on power usage by around 60 to 70 percent without sacrificing brightness levels. Recent studies from 2024 looked at five different auto manufacturing facilities and found that collectively these plants saved about four point two million dollars each year in their production areas covering nearly 3.8 million square feet. What makes this even better for businesses is that unlike traditional metal halide lamps which need new ballasts replaced roughly once every twelve to eighteen months, LED systems just keep working without those regular maintenance costs. This alone can slash overall ownership expenses by almost 40% when looking at a ten year period according to research published by Stouch Lighting last year.
Reducing Downtime with Long-Lasting, Standards-Compliant Fixtures
Work lights rated at IP65 or IP66 can handle dust storms and powerful water jets, which is why they're so popular in food processing plants and cleanrooms where hygiene matters most. Plants that switch to these tough LED options see around 83 percent less unexpected maintenance compared to old fluorescent setups, plus these lights last way longer too, often past the 50,000 hour mark. Take a steel factory somewhere in the Midwest as an example. Before switching to LED bay lights with thermal protection that meet those ANSI/IES standards, they were losing about 14 hours every month due to lighting problems. After installation, that number dropped down to roughly 2.6 hours per month. The difference in downtime adds up fast when running heavy machinery all day long.
ROI Analysis After Retrofitting Legacy Systems with Modern LED Work Light Solutions
The return on investment for industrial LED retrofits typically occurs within 2.1 to 3.4 years, driven by energy savings, reduced labor costs, and available utility incentives. According to a 2024 manufacturing efficiency report, facilities realize an average lifetime savings of $8.10 per square foot after conversion. Key contributors include:
- 70% lower kWh consumption versus HID lighting
- 50% accelerated depreciation under MACRS tax provisions
- Average industrial electricity rate of $0.12/kWh (EIA 2024)
Integrating smart controls such as occupancy sensing and daylight harvesting further reduces energy use by 18–34%, shortening payback periods by 5–8 months. These intelligent systems represent the next evolution in industrial lighting efficiency and operational intelligence.
FAQ
Why are LED high bay lights preferred over traditional lighting systems in industrial settings?
LED high bay lights are energy efficient, reduce electricity costs, require less maintenance, and provide better lighting quality without delays in turning on, which makes them ideal for industrial settings.
How do LED lights contribute to worker productivity?
Improved lighting from LED sources reduces eye strain and enhances visibility, allowing workers to perform tasks more efficiently and safely, which in turn can boost overall productivity.
What is the benefit of using smart LED high bay systems with motion sensors?
Smart LED systems with occupancy sensors adjust lighting based on activity and natural light levels, leading to significant energy savings and lowered operational costs.
What role does color temperature play in industrial lighting?
Color temperature, especially in the 4000 to 5000K range, helps maintain alertness and precision, improving concentration and reducing mistakes in detailed work environments.
How durable are LED lights in harsh industrial conditions?
LED lights are designed to withstand dust, moisture, and vibrations, offering greater durability and longer lifespan compared to traditional lighting methods.
Table of Contents
-
LED High Bay Lights: The Core Solution for Industrial Work Light Applications
- What Are LED High Bay Lights and How Do They Support Industrial Lighting Design?
- Key Differences Between High Bay and Low Bay Lighting in Manufacturing Facilities
- Brightness and Lumens in Industrial Lighting: Matching Output to Workspace Needs
- Case Study: LED Factory Lighting Upgrade in an Automotive Assembly Plant
- Trend Analysis: Shift Toward Smart LED High Bay Systems with Motion Sensors
- Illuminance, Uniformity, and Compliance with Industrial Lighting Standards
- Color Temperature and CRI: Optimizing Visual Clarity and Worker Performance
- Durability and Reliability of LED Work Lights in Harsh Industrial Conditions
- Energy Efficiency, Maintenance Reduction, and ROI of Industrial LED Work Lights
-
FAQ
- Why are LED high bay lights preferred over traditional lighting systems in industrial settings?
- How do LED lights contribute to worker productivity?
- What is the benefit of using smart LED high bay systems with motion sensors?
- What role does color temperature play in industrial lighting?
- How durable are LED lights in harsh industrial conditions?

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 NL
NL
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 IT
IT
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 GA
GA
 MI
MI
