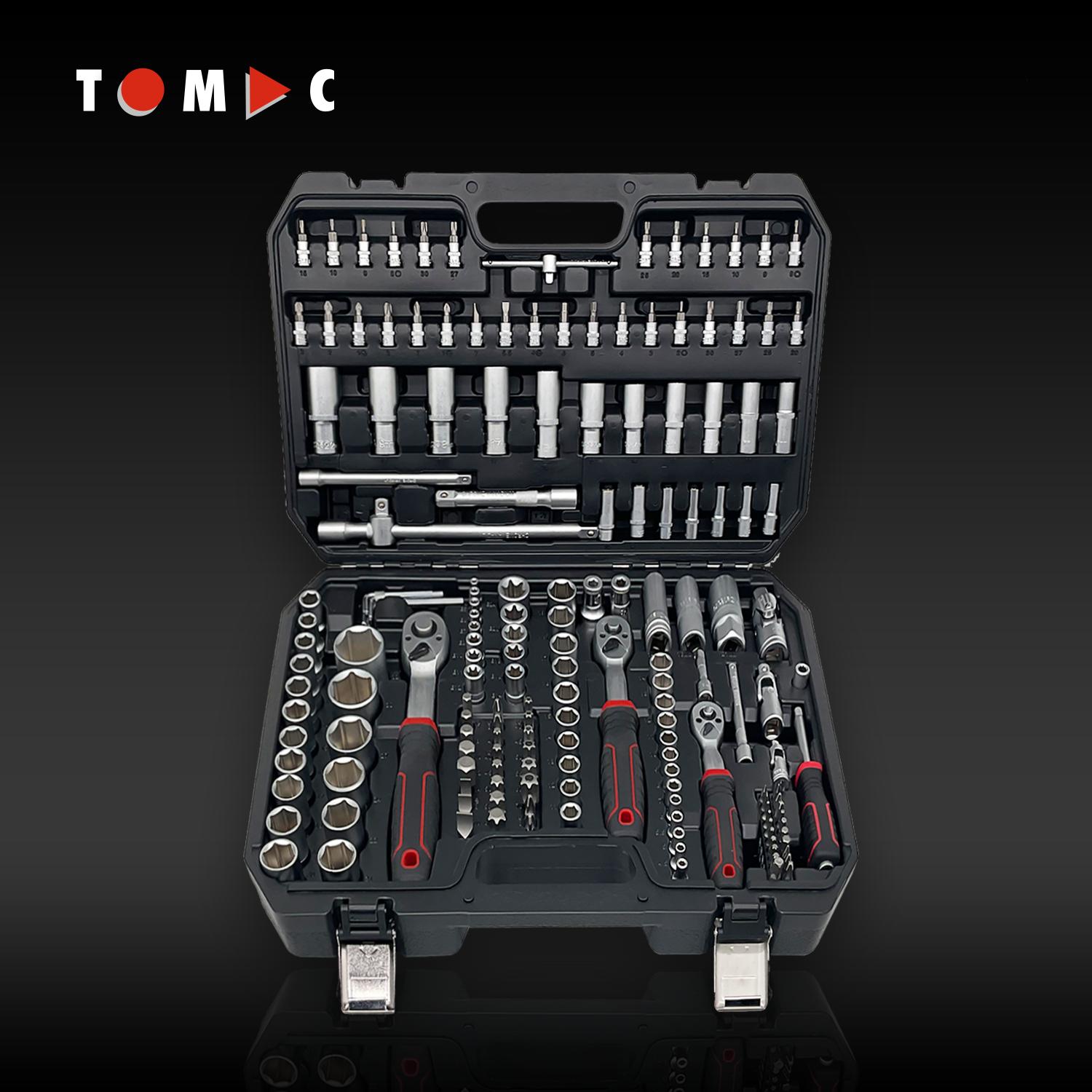
Understanding Socket Wrench Types and Core Components
Standard vs Deep Sockets: When to Use Each Type
Regular sockets work great for bolts that sit right on top of things, giving good hold without much space between them. Deep sockets run about two to three times longer than regular ones, making them perfect for getting at those stubborn nuts buried inside car engines or industrial equipment. Most mechanics grab an extension bar along with these long sockets when tackling tricky spots like wheel hubs or suspension parts where regular tools just won't reach. The extra length makes all the difference when dealing with tight spaces under vehicles or machinery frames.
Impact Socket Sets for High-Torque Applications
Built for use with pneumatic tools and high-torque demands, impact sockets feature thicker walls and chrome-molybdenum construction to endure sudden torque spikes exceeding 1,000 ft-lbs (Industrial Tool Standards 2023). These sockets resist fracturing during the removal of seized lug nuts or crankshaft bolts, making them essential in heavy-duty environments.
Specialty Sockets: Wheel Nut, Spark Plug, and Insulated Variants
| Socket Type | Key Feature | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Wheel nut sockets | Thin-walled design | Lug nut removal |
| Spark plug sockets | Internal rubber insert | Protecting ceramic insulators |
| Insulated variants | 1,000V dielectric coating | Electrical system maintenance |
Core Components: Sockets, Ratchets, Extension Bars, and Universal Joints
A complete socket wrench system relies on four key components working together. Ratchets with 72-tooth mechanisms allow a 5° arc swing, enabling operation in tight spaces. Universal joints maintain alignment with angled fasteners, while extension bars increase reach. Professionals recommend pairing 3/8" drive sets with 6" extensions for optimal versatility.
Material Quality: Chrome Vanadium vs Chrome-Molybdenum Durability
Chrome vanadium sockets (HRC 52–55 hardness) offer good corrosion resistance and are suitable for hand tool applications at a lower cost. For impact tools, chrome-molybdenum alloys (HRC 60+) are superior, providing 40% greater fatigue resistance under repeated stress cycles, as confirmed by metallurgical testing.
Choosing the Right Socket Sizes: Metric vs SAE Systems
Key differences between SAE and metric socket wrench sets
The SAE or Society of Automotive Engineers system works with imperial measurements using fractions of inches, compared to metric sets which go by millimeters instead. Most mechanics still see SAE tools showing up in older American cars and equipment made before 2000. Meanwhile, metric has become pretty much standard across newer vehicles worldwide these days. According to some recent data from 2023, around 78 percent of mechanics deal with both types of sockets on a regular basis. That means being able to tell them apart matters quite a bit if we want to avoid stripping bolts and causing unnecessary damage during repairs.
Common socket sizes in SAE and metric systems
| SAE (Inches) | Metric (Millimeters) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 3/8" | 10mm | Small engine components |
| 1/2" | 13mm | Lug nuts, suspension parts |
| 5/8" | 16mm | Heavy-duty industrial fasteners |
| 7/8" | 22mm | Agricultural equipment |
How to measure fasteners to determine correct socket size
Digital calipers are great for measuring the distance from flat to flat on those hexagonal bolt heads, or if we're dealing with square ones, just check the diagonal width instead. Now when working with old bolts that show signs of wear or corrosion, grabbing a thread pitch gauge becomes really important because it tells us what size they originally were meant to be. Sometimes measurements don't quite match up exactly with standard sizes. That's where experienced technicians usually suggest going with the next size up in increments of about half a millimeter or roughly 1/32 inch. This small adjustment makes all the difference in getting things to fit right without any risk of them slipping out later on.
Why many professionals need both metric and SAE sets
Workshops these days deal with all sorts of mixed measurement standards. Take Japanese bikes for instance they might have metric bolts on the engine but SAE fittings on the frame. Classic American muscle cars present similar challenges too, with SAE parts in the mechanical systems and metric connections in their electrical components. Keeping tools for both systems handy cuts down on those frustrating pauses when switching between measurements. Mechanics report losing somewhere around 12 to 15 minutes every hour just dealing with conversion issues during mixed standard repairs, according to industry surveys.
Socket Wrench Drive Sizes: Matching Tool to Task
Selecting the right drive size ensures efficient torque transfer and prevents tool failure. The three most common drive sizes serve distinct purposes:
- 1/4-inch drive: Best for precision tasks involving small fasteners (4mm–13mm), such as electronics, appliances, or compact engine areas. Handles up to 25 Nm of torque (HowACarWorks 2023).
- 3/8-inch drive: The go-to choice for automotive repairs on fasteners from 7mm to 19mm, balancing torque capacity (90–180 Nm) with access to confined spaces.
- 1/2-inch drive: Delivers high torque (180–450 Nm) for demanding jobs like suspension work and wheel nut removal, typically using 10mm+ sockets.
When to Use 1/4-Inch, 3/8-Inch, or 1/2-Inch Drive Sets
Match drive size to fastener dimensions and torque needs:
| Drive Size | Fastener Range | Typical Applications | Max Torque* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4" | 4mm - 13mm | Small engine repair, electronics | 25 Nm |
| 3/8" | 7mm - 19mm | Automotive repairs, HVAC systems | 180 Nm |
| 1/2" | 10mm - 24mm | Heavy-duty mechanical work | 450 Nm |
*Based on industry-standard chrome vanadium ratchet testing
For plumbing or electrical tasks requiring insulated tools, experts recommend 3/8" drive sets with non-conductive sockets to ensure safety without sacrificing usability.
Compatibility of Drive Sizes With Ratchets and Power Tools
Modern ratchets and power tools use standardized square drives, but compatibility depends on application:
- 1/4" drive adapters integrate with electric screwdrivers for low-torque assembly tasks.
- 3/8" drive systems connect to 90% of pneumatic impact wrenches used in service shops.
- 1/2" drive ratchets typically include reinforced gears to withstand industrial torque guns.
Always match the drive size to your tool’s output—using undersized drives with high-torque impact wrenches increases failure risk by 72% (Industrial Tool Safety Report 2024).
Evaluating Ratchet Performance and Ergonomic Design
Choosing a reliable socket wrench set requires assessing ratchet performance and ergonomic design to balance efficiency and user comfort.
Ratchet Tooth Count and Its Impact on Maneuverability
Ratchets with higher tooth counts (72+ teeth) enable tighter swing arcs of 3°–5°, crucial for navigating cramped spaces like engine bays. Coarser 24-tooth models handle heavy loads more effectively. According to Machine Design: An Integrated Approach, premium ratchets maintain consistent engagement through 10,000+ cycles—essential for professional durability.
Quick-Release Mechanisms and Ergonomic Handle Design
Quick-release buttons cut socket-swap time by 60% compared to traditional retaining pins. Handles with contoured grips and oil-resistant textures improve control, while ergonomic designs reduce hand fatigue by 40% during prolonged use, as shown in field studies.
Precision Engineering for Secure Fit on Fasteners
Dual-pawl mechanisms distribute load evenly across gear teeth, reducing wear. Precision-machined components and hardened steel springs help prevent fastener rounding—even after extensive use on rusted or stubborn bolts, ensuring long-term reliability.
Application-Specific Tips and Modern Innovations in Socket Wrench Sets
Automotive Repair: Selecting the Right Socket Wrench Set
When working on cars, it makes sense to get socket sets with both SAE and metric sizes since mechanics deal with everything from old American muscle cars to modern imports these days. Those universal joint sockets really come in handy when trying to reach tight spots in engines, and there are special ones made just for spark plugs too. Most experienced technicians stick with 6-point sockets when dealing with things that need serious torque, such as wheel lug nuts or suspension components. The reason? They're less likely to round off compared to other types, which saves time and headaches down the road.
Electrical Work and the Need for Insulated Socket Sets
Insulated socket sets rated for 1,000V provide critical protection against electric shock during live-panel servicing or industrial maintenance. Featuring thick dielectric coatings and non-conductive handles, these tools comply with IEC 60900 safety standards.
Working in Confined Spaces: Low-Profile and Flexible Options
Low-profile ratchets with 90-tooth mechanisms achieve 4° swing arcs, ideal for dashboard or firewall-side repairs. Magnetic extensions and 5" universal joints enhance reach into transmission or chassis areas without damaging fastener heads.
Smart Socket Sets with Torque Feedback and Digital Integration
Advanced smart sockets equipped with strain gauges and Bluetooth connectivity alert users when preset torque levels are reached, with ±2% accuracy. These systems automatically record torque data for quality assurance, warranty claims, and compliance documentation.
Lightweight Materials, Anti-Slip Coatings, and Modular Systems
Aircraft-grade aluminum sockets reduce overall toolkit weight by 30% compared to traditional chrome-vanadium models. Modular rail organizers with color-coded sections allow quick drive-size transitions while maintaining anti-corrosion protection and job-site efficiency.
FAQ
What are deep sockets, and when should they be used?
Deep sockets are about two to three times longer than regular sockets. They are ideal for accessing nuts buried inside car engines or industrial equipment.
What advantages do impact socket sets offer?
Impact socket sets, made from chrome-molybdenum, are designed for high-torque applications and resist fracturing during the removal of seized fasteners.
Why is it important to have both metric and SAE socket sets?
Many mechanics encounter both metric and SAE fasteners in their work, especially when dealing with vehicles that have components using different measurement systems.
What are the benefits of ratchets with higher tooth counts?
Ratchets with higher tooth counts enable tighter swing arcs, improving maneuverability in cramped spaces like engine bays.
How do digital calipers help in determining socket size?
Digital calipers measure the distance across bolt heads, helping users determine the correct socket size needed for tasks.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Socket Wrench Types and Core Components
- Choosing the Right Socket Sizes: Metric vs SAE Systems
- Socket Wrench Drive Sizes: Matching Tool to Task
- When to Use 1/4-Inch, 3/8-Inch, or 1/2-Inch Drive Sets
- Compatibility of Drive Sizes With Ratchets and Power Tools
- Evaluating Ratchet Performance and Ergonomic Design
- Application-Specific Tips and Modern Innovations in Socket Wrench Sets
- FAQ

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 NL
NL
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 IT
IT
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 GA
GA
 MI
MI
